This chapter provides you with information on features of Dr.Web for UNIX mail servers integration with different mail transfer systems.
Three methods of Dr.Web for UNIX mail servers integration are available. They are shown in the following picture (the fourth integration method, presented in the picture, is combined).
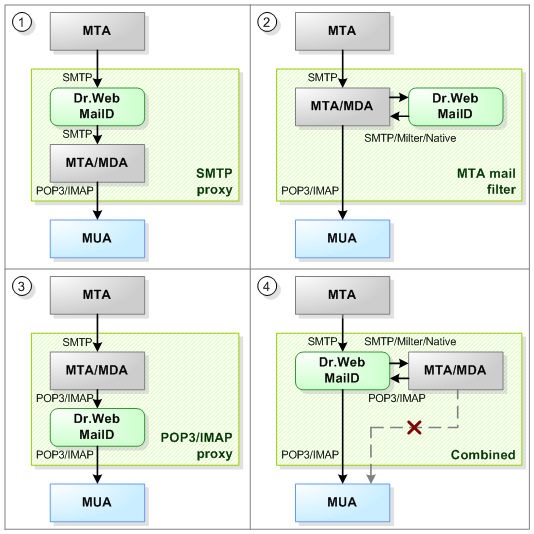
Picture 20. Methods to integrate Dr.Web for UNIX mail servers with mail systems
Note that all methods to integrate Dr.Web for UNIX mail servers directly with mail systems use only only components mail processing – Dr.Web MailD.
1.SMTP/LMTP proxy integration. Basic integration method, which is universal and applicable to all cases. It is suitable for integration with any MTA, as the method uses only standard mail protocols SMTP/LMTP. In this case, Dr.Web MailD is a proxy between an external MTA, which sends mail correspondence to the server, and an internal MTA/MDA, which is responsible for further storage of checked email messages and interaction with recipients (MUA) or transmitting messages to other mail systems. When required, you can also use this mode in order to organize checking of messages in SMTP Callback mode (note that for this the additional settings are required).
Note that this integration method does not require a protected MTA to run on the same server where Dr.Web for UNIX mail servers operates. For details on how to configure this integration method, refer to Working in SMTP/LMTP Proxy Mode.
2.MTA Mail filter integration. When this integration method is used, mail system performs communication with external MTAs that send mail correspondence to the server. Moreover, mail system is responsible for storage of checked email messages and communicates with message recipients (MUA). At that, Dr.Web MailD is used only as an external application-filter that checks received messages transmitted by the mail system. Dr.Web MailD returns check results and they determine further actions to be applied to the message.
For interaction between Dr.Web MailD and mail system in the filter mode, both standard protocols (for example, Milter and SMTP) and native protocols specific to the certain mail system can be used. For that, Dr.Web MailD includes special interaction plug-ins, implemented for connection to some mail systems in the filter mode. In this mode, Dr.Web MailD can be integrated with the following mail systems:
•CommuniGate Pro (see Description of integration configuration);
•Sendmail (see Description of integration configuration);
•Postfix (see Description of integration configuration);
•Exim (see Description of integration configuration);
•Qmail (see Description of integration configuration);
•Courier (see Description of integration configuration);
•Zmailer (see Description of integration configuration);
When it is possible to integrate Dr.Web MailD with a mail system, the MTA Mail filter mode is preferred to the SMTP proxy universal mode, as the filter mode requires less load on calculating server capacity: in this case, Dr.Web for UNIX mail servers performs only anti-virus and anti-spam functions and is not responsible for receiving and sending mail correspondence.
The MTA Mail filter integration method assumes that the protected MTA is running on the same server where Dr.Web for UNIX mail servers operates.
3.POP3/IMAP proxy integration. In this mode, Dr.Web for UNIX mail servers is used for message check upon transferring the message to the MUA of the end recipient via IMAP or POP3 mail protocol (and not at the moment when the message is received). This integration solution can be implemented only if the mail system protected with Dr.Web for UNIX mail servers is not a proxy but is finite, meaning that the system serves requests from the end MUA.
In this case, Dr.Web for UNIX mail servers is embedded as a proxy between MUA and MDA and transfers messages returned to MDA at the MUA request to check them by Dr.Web MailD. This method does not require MDA and MUA to run on the same server as Dr.Web for UNIX mail servers does. For details on how to configure this integration method, refer to Working with POP3/IMAP Mail Clients.
4.Combined integration. This mode is a combination of either the first or the second mode (any of them) with the third mode. Thus, it is possible, although not always reasonable, to implement double message check - when a message is received on the protected MTA/MDA and when the message is transferred from MDA to MUA. This integration method can be useful if some of the messages are sent through MTA further (and they must be checked on the SMTP level), but for the rest of the messages this MTA is the end MDA and they can be checked by request from the end MUA upon receipt.
Note that in this case fine tuning of the Dr.Web MailD operation logic is required, including specification of message processing Rules and, probably, rules for routing the outgoing mail (set in the Router parameter) in Sender settings.
To simplify the integration process, Dr.Web for UNIX mail servers includes installation packages and configuration scripts for different mail systems.
The configure_mta.sh script is responsible for setting up interaction between Dr.Web for UNIX mail servers and the currently used mail system. After startup, the script checks whether the required mail system is installed. If it appears to be missing, the script finishes its operation. If the required mail system is installed, the script asks the user several questions on essential settings for basic setup. Setup can be performed manually as well (for details, refer to the corresponding chapters of this manual).
The configure_mta.sh script configures MTA as follows:
•Connection using special transport is performed for Exim
•After-Queue Mode configuration is performed for Postfix
•Zmailer is configured to be used in context filter mode at the stage of SMTP-session
•Proxy scheme is performed for Qmail.
Thus, for example, to set Postfix to operate using Milter protocol, configure MTA according to the steps described in the corresponding section instead of running the configure_mta.sh script.