By default, the component is run automatically upon Dr.Web for UNIX File Servers startup. When run, the component structures data according to the structure described in MIB Dr.Web and waits for requests to receive data from external SNMP managers. The component receives information on the status of the program components and notifications on detected threats directly from the configuration daemon Dr.Web ConfigD, as shown in the picture below.
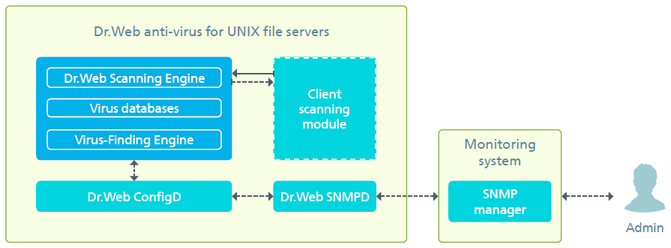
Picture 47. Component operation scheme
Threats can be detected by the scanning engine during the scanning initiated by Dr.Web for UNIX File Servers components; thus, the scheme contains an abstract "client scanning module". On threat detection, the appropriate count (of this threat type) is incremented by one and all SNMP managers that can receive notifications get an SNMP trap notifying on the detected threat.
Integration with the system SNMP agent
To enable correct operation of Dr.Web SNMP agent if the main system SNMP agent snmpd (net-snmp) already operates on the server, configure transmission of SNMP requests through the Dr.Web MIB branch from snmpd to Dr.Web SNMPD. For that purpose, edit the snmpd configuration file (usually for Linux the file is as follows: /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf), by adding the following string:
proxy -v <ver> -c <community> <host>:<port> <MIB branch>
where
•<ver> - used SNMP version (2c, 3);
•<community> - "community string" used by Dr.Web SNMPD.
•<host>:<port> - address listened by Dr.Web SNMPD.
•<MIB branch> - OID of the MIB branch. OID contains description of variables and traps used by Dr.Web (.1.3.6.1.4.1.29690).
When using settings of Dr.Web SNMP agent. The added string is as follows, by default:
proxy -v 2c -c public localhost:50000 .1.3.6.1.4.1.29690
Note that as port 161 is used by the main system SNMP agent snmpd in this case, it is required to specify another port for Dr.Web SNMPD in the ListenAddress parameter (in this example, 50000).