Operating Principles


|
Operating Principles |



|
|
The component is designed to request data from directory services (like Active Directory) and other data storages that support the LDAP protocol. Upon request, the received data (for example, users’ identifiers and rights) is transferred to Dr.Web for UNIX Mail Servers‘s components to be used in different rules for checks (for example, to allow a user to access a requested URL and etc.).
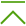
The Dr.Web LookupD component is launched automatically by the Dr.Web ConfigD configuration daemon when required (i.e. upon receiving a request for data). The diagram of the component’s operation is shown in the figure below.
Figure 24. Diagram of the components’ operation Upon receiving a data request from any of the components (, for example, Dr.Web Firewall for Linux or Dr.Web MailD), the Dr.Web ConfigD configuration daemon starts Dr.Web LookupD (if it has not been started yet). Then the component makes a request to the required data source and returns a reply (usually a list of strings which meet the search criterion). In Dr.Web LookupD‘s settings you can specify an unlimited number of data sources. When forming a request for data retrieval, the client component must specify the source for data. Once Dr.Web LookupD is started, it will operate for some time waiting for new requests. If there are no more requests, after a waiting period Dr.Web LookupD shuts down automatically. The basic way in which other components of the product use Dr.Web LookupD is for retrieving some data needed to check the validity of some conditions specified in the operation rules for these components. When checking the applicability of rules and the validity of conditions, data requests to Dr.Web LookupD are performed automatically. |