Operating Principles


|
Operating Principles |



|
|
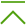
The Dr.Web ICAPD component uses the ICAP protocol (the Internet Content Adaptation Protocol described in RFC 3507) to interact with a proxy server, which is external with respect to Dr.Web for UNIX Internet Gateways and which handles HTTP/HTTPS connections from LAN hosts to web servers. From the proxy server, the component receives tasks to check (“to adapt”, in ICAP terms) the requests sent from local hosts to servers, and responses, received from the servers. If a user request contains a URL that is included into the black list or belongs to any of the unwanted categories of web resources, Dr.Web ICAPD instructs the proxy server to break the connection with the web server and to return to the client an HTML page generated by Dr.Web ICAPD using a template which is supplied together with the component. The page contains a message informing the user that the access to requested resource is denied, and a description of the denial reason. A similar page is generated and then returned to a user by the proxy server if Dr.Web ICAPD detects a threat to be blocked in the web server’s response. A diagram showing the operation of this component is given in the figure below.
Figure 11. Diagram of the components’ operation To check whether any given URL belongs to any of the categories, the component not only uses the database of web resource categories, which is updated regularly from Doctor Web’s update servers, but also refers to the Dr.Web Cloud service. Doctor Web keeps track of the following web resources categories: •InfectionSource—websites containing malicious software (“infection sources”). •NotRecommended—fraudulent websites (that use “social engineering”) visiting which is not recommended. •AdultContent—websites that contain pornographic or erotic materials, dating sites, etc. •Violence—websites that encourage violence or contain materials about various fatal accidents, etc. •Weapons—websites that describe weapons and explosives or provide information on their manufacturing. •Gambling—websites that provide access to online games of chance, casinos, auctions, including sites for placing bets, etc. •Drugs—websites that promote use, production or distribution of drugs, etc. •ObsceneLanguage—websites that contain the obscene language (in titles, articles, etc.). •Chats—websites that offer a real-time transmission of text messages. •Terrorism—websites that contain aggressive and propaganda materials or terroristic attacks descriptions, etc. •FreeEmail—websites that offer the possibility of free registration of a web mailbox. •SocialNetworks—different social networking services: general, professional, corporate, interest-based; thematic dating sites. •DueToCopyrightNotice—websites that were specified by the holders of copyrights pertaining to content or works protected by copyright law (movies, music, etc.). In the settings, the system administrator can specify the categories of web resources users’ access to which is unwanted. It is also possible to configure one’s own black lists to block the access to the necessary web resources, and white lists to allow access for users. The access to the web resources included into white lists will be allowed, even if they belong to the unwanted categories. If there is no information about a URL in the local black lists and the local database of web resource categories, the program refers to the Dr.Web Cloud service. It allows the program to check whether any information is available about the maliciousness of the URL. Such information is received from other Dr.Web’s products on a real-time basis.
The Dr.Web Updater component is used to regularly and automatically update the databases of web resource categories from Doctor Web update servers. The same component is used to update virus databases for the Dr.Web Scanning Engine scanning engine. The Dr.Web CloudD component is used to refer to Dr.Web Cloud service (using of the cloud service is configured in Appendixes common settings and can be disabled, if necessary). To check transferred data, Dr.Web ICAPD uses the Dr.Web Network Checker component. The latter one initiates scanning via the Dr.Web Scanning Engine scanning engine. |